Alcohol, although widely accepted and enjoyed by many, can have detrimental effects on your health. From liver damage to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety, consuming excessive amounts of alcohol can lead to a myriad of health problems. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which alcohol can negatively impact your well-being and delve into the importance of moderation when it comes to indulging in this popular social beverage. So grab a drink (preferably water) and join us as we shed light on the hidden dangers of excessive alcohol consumption.
Physical Health Problems
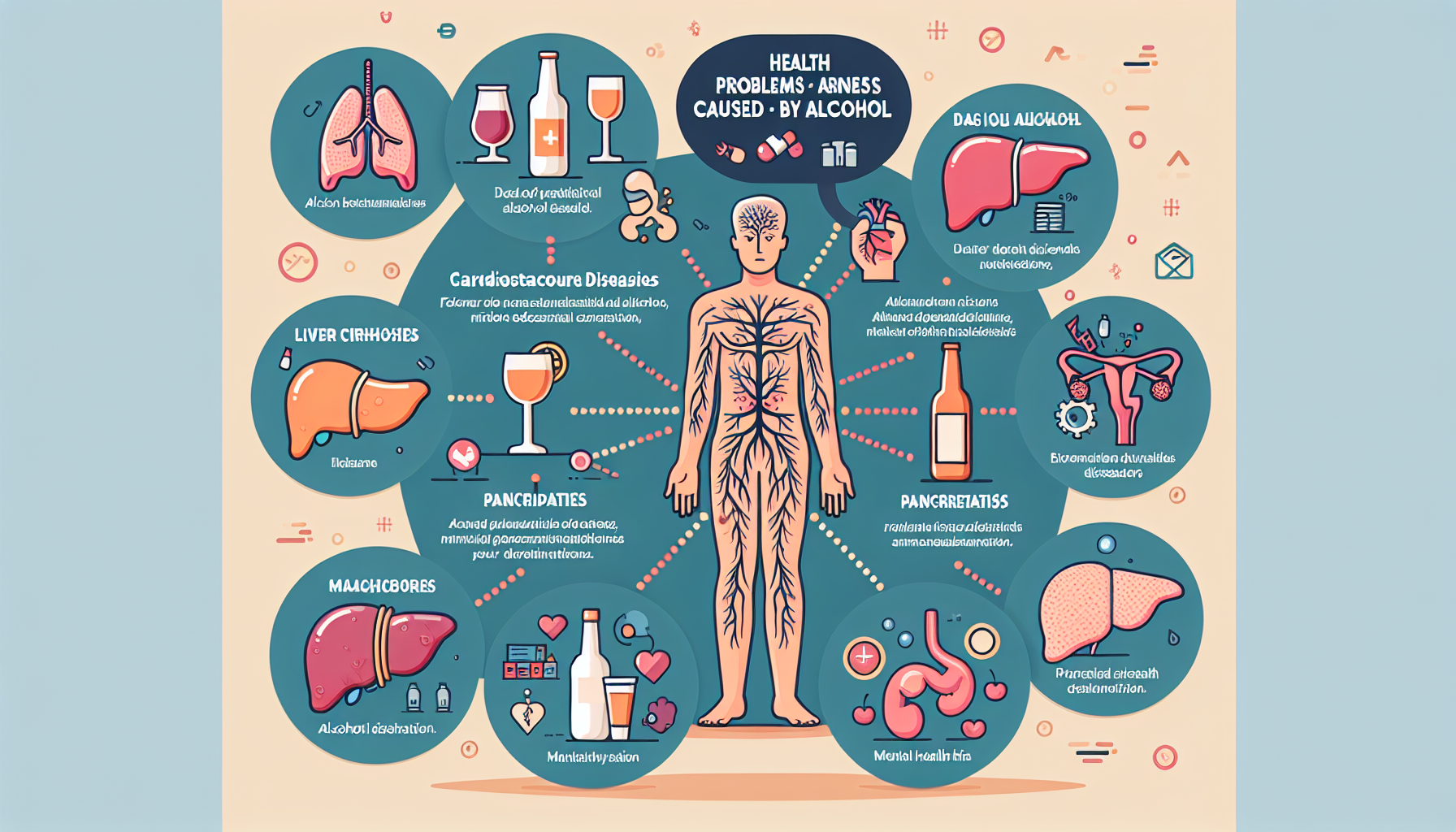
Liver Damage
Excessive alcohol consumption can have severe consequences on the liver. Over time, alcohol abuse can lead to liver diseases such as alcoholic hepatitis, alcoholic fatty liver disease, and even cirrhosis. These conditions can cause inflammation, scarring, and irreversible damage to the liver tissue, impairing its ability to function properly. The liver is responsible for detoxifying harmful substances in the body, so when it is damaged, toxins can build up, causing further health issues.
Cardiovascular Issues
Alcohol abuse can have detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system. Chronic heavy drinking can increase the risk of high blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, weakened heart muscles, and even heart failure. Additionally, alcohol can raise cholesterol levels and contribute to the formation of blood clots, which can increase the risk of stroke or heart attack. It is important to note that even moderate alcohol consumption can have negative cardiovascular effects.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
The digestive system is also negatively impacted by excessive alcohol consumption. Alcohol can irritate the lining of the stomach and intestines, leading to various gastrointestinal disorders. This includes gastritis, which is inflammation of the stomach lining, and peptic ulcers, which are painful sores that develop in the stomach or upper part of the small intestine. Chronic alcohol abuse may also contribute to an increased risk of developing pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas.
Pancreatic Complications
Alcohol abuse can significantly harm the pancreas, an organ responsible for producing enzymes essential for digestion and regulating blood sugar levels. Heavy drinking can lead to pancreatitis, a condition where the pancreas becomes inflamed and swollen. Chronic pancreatitis can cause permanent damage, resulting in impaired digestion and the potential development of diabetes.
Weakened Immune System
Excessive alcohol consumption weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and diseases. Alcohol can impair the function of immune cells and hinder their ability to fight off harmful bacteria and viruses. Consequently, those who engage in heavy drinking are more prone to respiratory infections, pneumonia, and other infections. Additionally, long-term alcohol abuse can lead to immunodeficiency, leaving individuals vulnerable to a range of health complications.
Mental Health Issues
Depression
Alcohol and mental health issues often go hand in hand. While individuals may turn to alcohol as a way to cope with feelings of sadness or depression, the long-term effects of alcohol on mental health can be devastating. Alcohol is a depressant, and excessive consumption can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to increased symptoms of depression. This can create a vicious cycle where alcohol is used as a temporary escape, but ultimately worsens the underlying mental health condition.
Anxiety
Alcohol can temporarily alleviate feelings of anxiety, but prolonged and heavy drinking can actually exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Alcohol disrupts the natural balance of chemicals in the brain, leading to increased anxiety levels and heightened feelings of unease. Additionally, the withdrawal effects of alcohol can trigger severe anxiety and panic attacks in those dependent on alcohol.
Psychosis
Chronic heavy drinking can also lead to alcohol-induced psychosis, a severe mental condition characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and impaired cognitive function. These symptoms may be temporary or long-lasting, depending on the extent of alcohol abuse. Alcohol-induced psychosis can significantly impact an individual’s ability to function in daily life and may require medical intervention and treatment.

Addiction and Substance Abuse
Alcohol Use Disorder
Alcohol abuse can progress into an alcohol use disorder (AUD), a chronic condition characterized by the inability to control or stop drinking despite negative consequences. AUD is a serious medical condition that can affect all aspects of a person’s life and overall well-being. It is crucial to seek professional help if you or someone you know is struggling with AUD.
Substance Abuse
In addition to alcohol, individuals with alcohol addiction may be prone to substance abuse involving other drugs as well. The co-occurrence of alcohol and substance abuse can further worsen the physical and mental health complications associated with addiction.
Neurological Disorders
Alcohol-Induced Brain Damage
Excessive alcohol consumption over a prolonged period can lead to alcohol-induced brain damage. This condition affects cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health. The brain’s structure and function are altered, leading to difficulties with learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. Moreover, alcohol-induced brain damage can contribute to behavioral changes, including impulse control issues and emotional instability.
Memory Loss
Alcohol abuse is closely linked to memory loss and impaired cognitive function. Heavy drinking can significantly disrupt memory formation and retrieval, leading to blackouts and gaps in memory. Over time, alcohol-induced memory loss can become more severe and impact an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks and maintain relationships.
Cognitive Impairment
Alcohol abuse can result in long-term cognitive impairment, affecting various cognitive abilities such as attention, concentration, and problem-solving skills. Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to a decline in overall cognitive function, impairing daily functioning and reducing the quality of life.

Increased Risk of Cancer
Oral Cancer
Alcohol consumption, particularly when combined with smoking, increases the risk of developing oral cancer. Heavy alcohol use damages the cells of the mouth and throat, making them more susceptible to cancerous growths. It is important to note that even moderate alcohol consumption can still contribute to an increased risk of oral cancer.
Liver Cancer
The liver is particularly vulnerable to the harmful effects of alcohol, and long-term alcohol abuse significantly increases the risk of developing liver cancer. Chronic liver inflammation and cirrhosis, which can be caused by excessive alcohol consumption, can progress into liver cancer. Regular screenings and reducing alcohol intake are crucial in reducing the risk of this highly dangerous form of cancer.
Breast Cancer
Studies have shown a correlation between alcohol consumption and an increased risk of breast cancer in women. Even low to moderate alcohol intake has been associated with an elevated risk. It is important for women to be aware of this risk factor and make informed decisions regarding their alcohol consumption.
Colorectal Cancer
Excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Regular heavy drinking can contribute to inflammation and damage in the colon, leading to the development of cancerous growths. Lowering alcohol intake and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
Social and Interpersonal Problems
Relationship Issues
Alcohol abuse can strain relationships, leading to interpersonal conflicts and breakdowns in communication. Frequent intoxication and the behavioral changes associated with alcohol consumption can negatively impact romantic relationships, friendships, and familial bonds. Seeking help and support can be essential in resolving relationship issues caused by alcohol.
Domestic Violence
Alcohol is often a contributing factor in instances of domestic violence. Alcohol abuse can lower inhibitions, increase aggression, and impair judgment, leading to violent behavior in relationships. It is vital to recognize the connections between alcohol abuse and domestic violence and seek assistance in breaking this devastating cycle.
Work-related Issues
Excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on work performance and stability. Frequent absenteeism, impaired judgment, decreased productivity, and strained relationships with colleagues can all result from alcohol abuse. It is important to address these work-related issues and seek support or treatment to regain control of one’s professional life.

Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is a severe condition that affects children whose mothers consumed alcohol during pregnancy. FAS is characterized by physical, cognitive, and behavioral abnormalities that can last a lifetime. These children may face difficulties with learning, memory, impulse control, and physical growth. It is critical for pregnant women to abstain from alcohol to prevent the development of FAS in their unborn children.
Alcohol-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder
Alcohol-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder (ARND) refers to a range of impairments that can affect a child whose mother drank alcohol during pregnancy. Children with ARND may experience difficulties with attention, problem-solving, impulse control, and social interaction. Early intervention and support are crucial in helping children with ARND reach their full potential.
Alcohol-Related Birth Defects
Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can lead to various birth defects, including heart defects, kidney abnormalities, facial malformations, and growth deficiencies. These alcohol-related birth defects can have a lifelong impact on the affected child’s health and well-being. It is vital for expecting mothers to understand the serious consequences of alcohol consumption during pregnancy and to avoid alcohol completely.
Accidents and Injuries
Drunk Driving Accidents
Drinking and driving is a dangerous combination that can lead to devastating accidents, injuries, and even loss of life. Alcohol impairs judgment, coordination, and reaction times, increasing the risk of motor vehicle accidents. The repercussions of drunk driving accidents can be lifelong, affecting not only the individuals involved but also their families and communities.
Alcohol-Related Falls
Alcohol can impair balance and coordination, making individuals more prone to falls and accidents. Falls resulting from alcohol intoxication can lead to severe injuries such as broken bones, fractures, and head traumas. It is essential to be mindful of the increased risk of falls when consuming alcohol and to ensure a safe environment to prevent these accidents.
Burns and Fires
The impaired judgment and coordination caused by alcohol can result in accidents involving burns and fires. Cooking mishaps, negligent use of flammable materials, and unsafe behavior around open flames can lead to severe burns and fire-related injuries. Practicing caution and responsibility when consuming alcohol is crucial in preventing such accidents.
Effects on Sleep and Fatigue
Insomnia
Alcohol disrupts normal sleep patterns and can contribute to insomnia. While alcohol may initially induce drowsiness, it inhibits the restorative aspects of sleep, such as rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Over time, alcohol-induced insomnia can lead to chronic sleep disturbances and long-term sleep disorders.
Disrupted Sleep Patterns
Regular alcohol consumption can disrupt the natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to irregular sleep patterns. Alcohol can cause frequent awakenings during the night, decreased overall sleep duration, and poor sleep quality. These disruptions can result in daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and a decreased ability to function optimally.
Daytime Fatigue
Alcohol’s impact on sleep quality can lead to persistent daytime fatigue and excessive sleepiness. Chronic fatigue can significantly impact daily activities, productivity, and overall quality of life. It is important to prioritize healthy sleep habits and seek professional help if alcohol-induced sleep disturbances persist.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to malabsorption of essential vitamins and minerals. Alcohol interferes with the body’s ability to absorb nutrients from food, potentially resulting in deficiencies. Vitamin deficiencies, particularly of vitamins B1, B6, and B12, can lead to neurological disorders and other health complications.
Malnutrition
Alcohol is high in empty calories and provides little to no nutritional value. Heavy and prolonged drinking can replace essential nutrients from a balanced diet, leading to malnutrition. Malnutrition can weaken the immune system, impair cognitive function, and contribute to a range of physical health problems. Proper nutrition and seeking professional guidance can help address and overcome alcohol-related malnutrition.
In conclusion, alcohol abuse can have a significant impact on both physical and mental health. From liver damage and cardiovascular issues to mental health disorders and increased cancer risk, the consequences of excessive alcohol consumption are wide-ranging and severe. It is important to prioritize one’s health and seek help and support when needed to overcome alcohol-related health problems. Remember, your well-being is precious, and taking steps towards a healthier lifestyle can lead to a happier and more fulfilling life.

