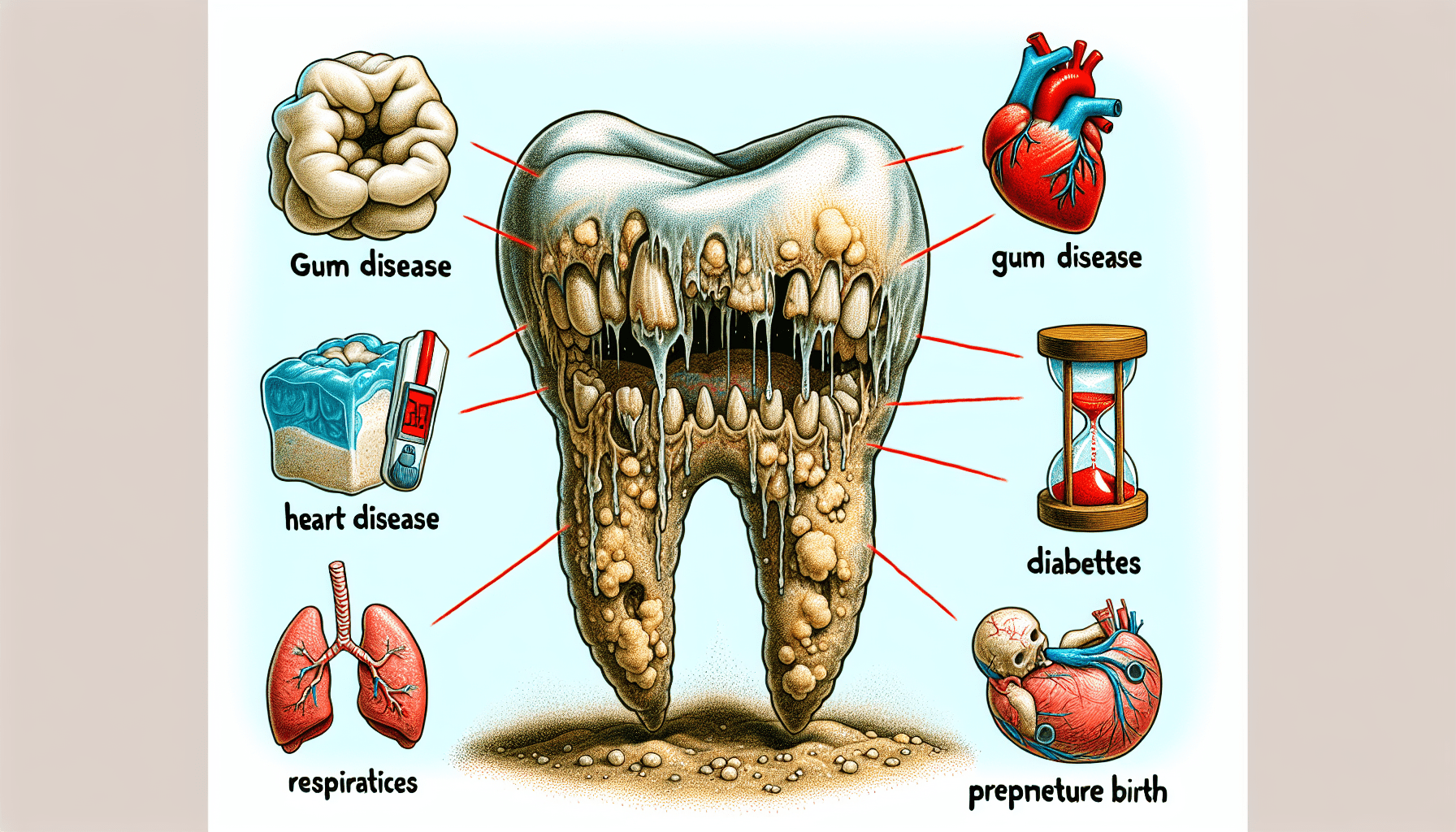
You may not realize it, but having bad teeth can lead to a whole host of health problems that extend beyond your mouth. From gum disease to heart disease, the condition of your teeth can have a significant impact on your overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the various health problems that bad teeth can cause, shedding light on the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene. By understanding the potential consequences, you’ll be motivated to take better care of your teeth and ensure a healthier future for yourself.
Cardiovascular Problems
Endocarditis
Endocarditis refers to the inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, known as the endocardium. While the condition can be caused by various factors, poor oral health can significantly increase the risk of developing endocarditis. When you have bad teeth or gum disease, the harmful bacteria present in your mouth can enter your bloodstream through bleeding gums or dental procedures. Once these bacteria reach the heart, they can cause inflammation and infection in the endocardium, leading to endocarditis. It is crucial to maintain good oral hygiene and seek prompt dental care to prevent the risk of developing this serious cardiovascular problem.
Heart Disease
Did you know that there is a significant link between oral health and heart disease? The health of your teeth and gums can have a direct impact on your cardiovascular system. Poor oral hygiene, gum disease, and chronic inflammation in the oral cavity can contribute to the development of heart disease. The bacteria present in your mouth can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation and damaging the blood vessels. This can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and stroke. Taking care of your oral health is not only crucial for your smile but also for the health of your heart.
Stroke
Stroke, a potentially life-threatening condition, occurs when there is a disruption in the blood supply to the brain. Research has shown that individuals with gum disease are more likely to have an increased risk of stroke. The bacteria present in your mouth can travel through the bloodstream and cause inflammation and clot formation in the blood vessels, leading to stroke. Maintaining good oral hygiene, scheduling regular dental check-ups, and promptly treating any oral health issues can help reduce the risk of stroke and protect your overall health.
Digestive Disorders
Tooth Loss and Nutritional Deficiencies
One might not immediately associate tooth loss with digestive disorders, but the connection between the two is noteworthy. When you have missing teeth, it becomes challenging to chew and properly break down food, leading to digestive problems. Moreover, individuals with missing teeth often avoid certain foods, leading to a restricted diet that may lack essential nutrients. This can result in nutritional deficiencies, affecting overall health. It is important to address tooth loss promptly with dental interventions such as dental implants or dentures to ensure proper digestion and maintain a balanced diet.
Gum Disease and Digestive Problems
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, does not only impact oral health but can also have consequences on your digestive system. The bacteria that cause gum disease can enter the digestive tract through saliva when swallowing. This can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to digestive problems such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). By maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking timely treatment for gum disease, you can promote a healthy digestive system and overall well-being.
Oral Bacteria and Digestive Health
The oral cavity is a complex ecosystem teeming with bacteria, both good and harmful. When there is an imbalance in the oral microbiome, it can have a negative impact on digestive health. The harmful bacteria associated with oral infections, such as tooth decay and gum disease, can travel through the digestive system and disrupt the natural balance of gut bacteria. This can result in digestive disorders and inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, can help maintain a healthy oral microbiome and support optimal digestive health.

Respiratory Infections
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection characterized by inflammation of the air sacs in the lungs. The link between oral health and pneumonia lies in the aspiration of oral bacteria into the lungs. When you have poor oral hygiene or untreated gum disease, the harmful bacteria present in your mouth can be inhaled into the lungs, leading to infection and pneumonia. Practicing good oral hygiene, especially by brushing your teeth and tongue regularly, can help reduce the risk of oral bacteria entering the respiratory system and lower the likelihood of developing pneumonia.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease that affects the airways and makes breathing difficult. Poor oral health, particularly gum disease, has been linked to an increased risk of COPD. The bacteria associated with gum disease can enter the respiratory tract, causing chronic inflammation and damage to the lungs. This can worsen COPD symptoms and lead to further complications. It is crucial for individuals with COPD to maintain good oral hygiene and regularly visit their dentist to manage any oral health issues effectively.
Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia occurs when foreign substances, such as saliva, food, or liquids, enter the lungs instead of being swallowed into the digestive system. Poor oral health, including tooth decay and gum disease, can increase the risk of aspiration pneumonia. When there are oral infections or untreated dental problems, the bacteria present in the mouth can be aspirated into the lungs, leading to infection and pneumonia. By maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking timely dental care, you can reduce the risk of aspiration pneumonia and protect your respiratory health.
Diabetes Complications
Gum Disease and Insulin Resistance
Diabetes and gum disease often go hand in hand. It has been observed that individuals with diabetes are more prone to developing gum disease, and vice versa. The harmful bacteria associated with gum disease can cause inflammation in the gums, leading to insulin resistance, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes. On the other hand, high blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes can contribute to the progression of gum disease. It is essential for individuals with diabetes to prioritize oral health and work closely with both their dentist and healthcare provider to manage blood sugar levels and minimize the risk of complications.
Impact on Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. However, untreated dental problems, such as tooth decay and gum disease, can disrupt blood sugar control. Inflammation in the oral cavity can lead to insulin resistance, making it more challenging to manage blood sugar levels effectively. It is essential to address any oral health issues promptly and establish good oral hygiene practices to support optimal blood sugar control and overall diabetes management.
Increased Risk of Diabetic Complications
Individuals with diabetes are already at an increased risk of various complications, including cardiovascular problems and nerve damage. However, poor oral health can further exacerbate these risks. The harmful bacteria associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation and damage to blood vessels and nerves. This can increase the risk of diabetic complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, and diabetic neuropathy. By prioritizing oral health and seeking regular dental care, individuals with diabetes can reduce the likelihood of developing these serious complications.

Joint Problems
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ)
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) connects your jawbone to your skull, allowing you to open and close your mouth. Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ) refers to a condition characterized by pain and dysfunction in this joint. Poor oral health, such as tooth loss or misalignment, can contribute to the development of TMJ disorder. Imbalance in the bite caused by missing teeth or misaligned jaws can put excessive strain on the TMJ, leading to pain, clicking sounds, and difficulty in jaw movement. Seeking dental treatment, including dental prosthetics or orthodontics, can help alleviate TMJ disorder and improve oral function and comfort.
Jaw Misalignment and Arthritis
Jaw misalignment, also known as malocclusion, can have a significant impact on your oral health and overall comfort. Misaligned jaws can lead to difficulties in biting, chewing, and speaking. Additionally, the improper distribution of forces on the jaw joint can result in temporomandibular joint (TMJ) arthritis. This can cause pain, inflammation, and even restricted movement of the jaw. Addressing jaw misalignment promptly with orthodontic treatments or dental appliances can help prevent TMJ arthritis and improve overall oral health.
Jaw Bone Loss and Joint Pain
Jaw bone loss, also known as osteoporosis of the jaw, can occur due to various reasons, including poor oral health and hormonal changes. When the jawbone weakens and loses density, it can contribute to joint pain and dysfunction. Weakening of the jawbone increases the risk of developing temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, leading to pain and restricted jaw movement. Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular dental check-ups, and ensuring an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D can help maintain strong jaw bones, minimize joint pain, and safeguard your oral health.
Oral Cancer
Link Between Oral Health and Cancer
Oral cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects various parts of the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, and throat. Maintaining good oral health is crucial for the prevention of oral cancer. Poor oral hygiene, tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection are common risk factors for oral cancer. Regular dental check-ups can help detect early signs of oral cancer and improve the chances of successful treatment. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a nutritious diet, abstinence from tobacco and alcohol, and practicing safe sex can further reduce the risk of developing oral cancer.
Oral Cancer Symptoms
Knowing the signs and symptoms of oral cancer can help in early detection and prompt intervention. Common symptoms of oral cancer include persistent mouth sores, lumps or thickening in the mouth or throat, difficulty in swallowing or chewing, changes in voice, unexplained bleeding, and persistent ear pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult your dentist or healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. Early detection and treatment significantly increase the chances of successful outcomes and improved overall prognosis.
Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are not just about maintaining a healthy smile; they play a vital role in overall health and well-being. Dentists are trained to detect early signs of oral health problems, including oral cancer. During your dental check-up, your dentist will perform a thorough examination of your mouth, including the gums, tongue, and throat, looking for any abnormalities or signs of disease. By scheduling regular dental check-ups, you can ensure early detection of any oral health issues and receive appropriate treatment to preserve your oral and overall health.

Compromised Immune System
Oral Infections and Immune Response
The immune system is responsible for protecting the body against infections and maintaining overall health. However, poor oral health can compromise the immune system’s ability to function effectively. When you have oral infections, such as gum disease or tooth abscesses, the immune system is constantly battling the bacteria and inflammation in the oral cavity. This constant immune response can weaken the overall immune system, making it more challenging to fight off other infections and illnesses. Practicing good oral hygiene and seeking timely dental care are essential to support a strong immune system and overall well-being.
Periodontitis and Systemic Inflammation
Periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease, is characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums and surrounding tissues. The inflammation associated with periodontitis can extend beyond the oral cavity, leading to systemic inflammation throughout the body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to various health problems, including an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. By effectively managing and treating periodontitis, you can reduce the burden of systemic inflammation and promote better overall health.
Impaired Ability to Fight Infections
Maintaining good oral health is essential for maintaining a strong immune system and the ability to fight off infections. When you have dental problems or oral infections, the bacteria present in your mouth can easily enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. This constant exposure to bacteria can overwhelm the immune system, impairing its ability to defend against other infections. By prioritizing oral hygiene, seeking regular dental check-ups, and promptly treating any oral health issues, you can support your immune system’s ability to fight off infections and ensure optimal overall health.
Issues with Pregnancy
Premature Birth
Pregnancy is a beautiful and transformative time, but it can also present certain risks, especially when it comes to oral health. Poor oral health has been associated with an increased risk of premature birth. The harmful bacteria from gum disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to the uterus, potentially triggering premature labor. Additionally, hormonal changes during pregnancy can make gums more susceptible to inflammation, further increasing the risk of gum disease. It is crucial for expectant mothers to prioritize oral hygiene, schedule regular dental check-ups, and promptly address any oral health issues to support a healthy pregnancy and reduce the risk of premature birth.
Low Birth Weight
Low birth weight is a common concern for expectant mothers, as it can contribute to various health problems for the baby. Studies have shown a potential link between poor oral health and low birth weight. Gum disease, which is characterized by inflammation and infection in the gums, has been associated with an increased risk of delivering a baby with low birth weight. By maintaining good oral hygiene, seeking regular dental care, and managing gum disease effectively during pregnancy, you can help reduce the risk of low birth weight and support the health and well-being of your baby.
Gestational Diabetes Risk
Gestational diabetes refers to high blood sugar levels that develop during pregnancy in women who did not have diabetes before. Poor oral health, particularly gum disease, has been linked to an increased risk of gestational diabetes. The inflammation associated with gum disease can affect insulin sensitivity, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Additionally, hormonal changes during pregnancy can make gums more susceptible to gum disease, further contributing to the risk of gestational diabetes. By prioritizing oral hygiene and seeking regular dental check-ups during pregnancy, you can minimize the risk of gestational diabetes and promote a healthy pregnancy.
Mental Health Impact
Social Anxiety and Low Self-esteem
Your oral health can significantly impact your mental well-being. When you have dental problems, such as missing teeth, misaligned jaws, or visible oral infections, it can lead to social anxiety and low self-esteem. The appearance of your smile plays a crucial role in your overall confidence and self-perception. Dental interventions, such as dental implants, orthodontic treatments, or cosmetic dentistry, can help enhance your smile, restore your confidence, and improve your mental well-being.
Depression and Oral Health
Depression is a common mental health condition that can have both causes and consequences related to oral health. The impact of depression on oral health can manifest in various ways. The lack of motivation and energy associated with depression can result in neglecting oral hygiene practices, leading to an increased risk of dental problems such as tooth decay and gum disease. On the other hand, individuals with poor oral health may experience embarrassment, pain, or difficulty eating, which can contribute to feelings of isolation and depression. It is important to address both mental health and oral health concerns in order to promote overall well-being.
Psychological Effects of Missing Teeth
Missing teeth can have significant psychological effects on an individual’s overall well-being. It can impact self-confidence, self-image, and social interactions. The gaps left by missing teeth can make individuals self-conscious about their smile, leading to social anxiety and avoiding social activities. In addition, the functional limitations caused by missing teeth can affect speech, chewing ability, and overall quality of life. Dental interventions, such as dental implants or dentures, can help restore missing teeth and improve psychological well-being by enhancing both appearance and oral function.
Systemic Inflammation
Link Between Oral Health and Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response by the body to fight off infections or repair damaged tissues. However, chronic inflammation can have detrimental effects on overall health. Poor oral health, including gum disease and oral infections, can contribute to systemic inflammation. The harmful bacteria associated with oral infections can enter the bloodstream, triggering an inflammatory response throughout the body. This chronic inflammation has been linked to an increased risk of various chronic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Maintaining good oral hygiene and promptly addressing any oral health issues can help minimize the risk of systemic inflammation and protect your overall health.
Periodontitis and Cardiovascular Inflammation
Periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease, is characterized by chronic inflammation and infection in the gums and surrounding tissues. The inflammatory response triggered by periodontitis goes beyond the oral cavity and can contribute to systemic inflammation. There is a growing body of evidence linking periodontitis to cardiovascular inflammation. The inflammation associated with gum disease can spread to the blood vessels, promoting the development of atherosclerosis and increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. By effectively managing and treating periodontitis, you can lower the burden of cardiovascular inflammation and promote better overall cardiovascular health.
Implications on Overall Health
The implications of poor oral health on overall health are far-reaching. The mouth serves as a gateway to the rest of the body, and the health of your teeth and gums can have a significant impact on your overall well-being. Chronic oral infections, such as tooth decay and gum disease, can lead to systemic inflammation, compromising the immune system and increasing the risk of various health problems. Additionally, the bacteria from oral infections can enter the bloodstream, affecting the health of vital organs, such as the heart and lungs. Prioritizing oral hygiene, scheduling regular dental check-ups, and seeking timely dental care are essential for safeguarding your overall health and well-being.

