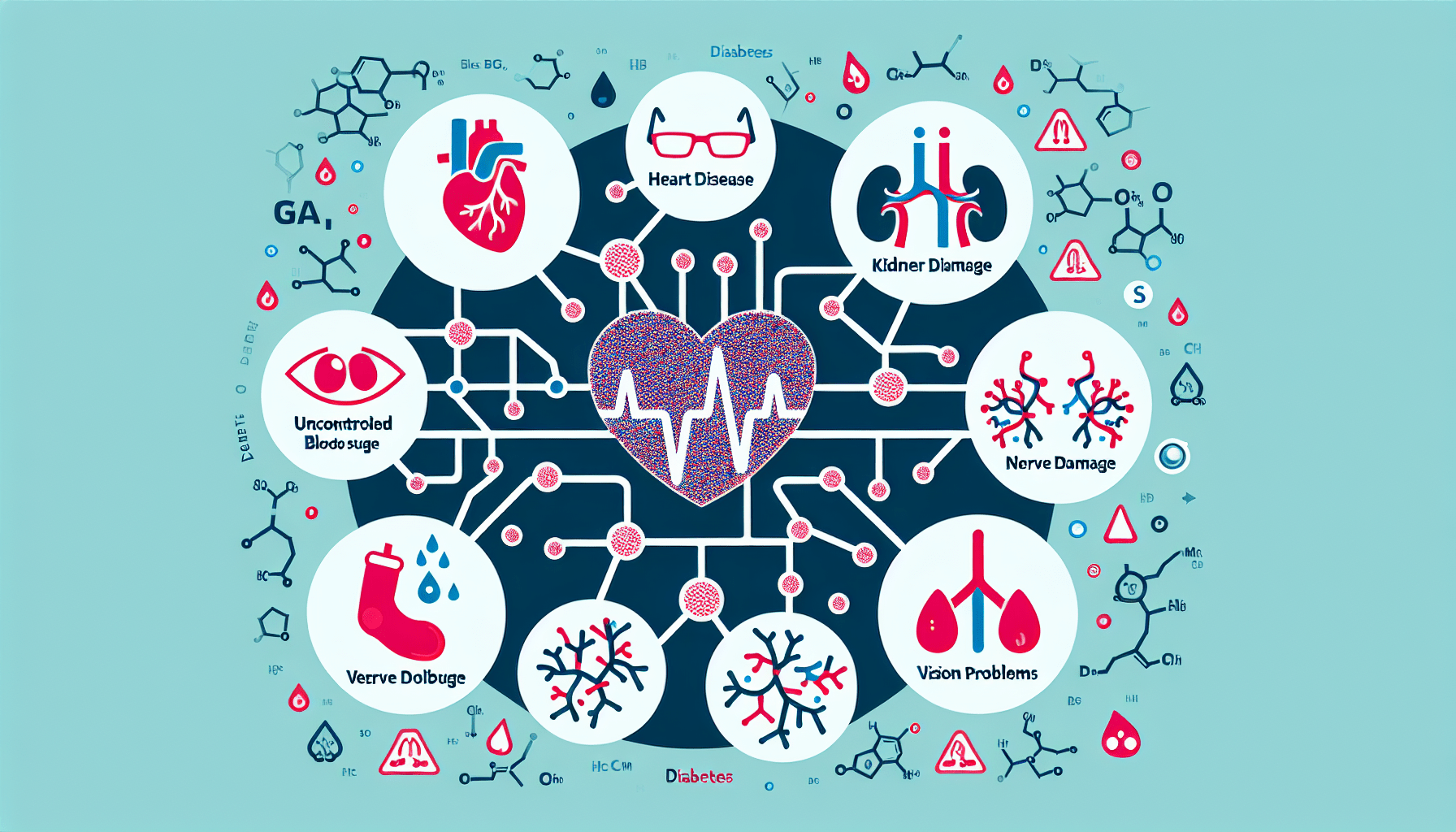
Living with diabetes can bring about various health complications that require careful management. From heart disease and stroke to kidney disease and nerve damage, this article explores the wide range of health issues that can be associated with diabetes. Understanding these potential complications is essential for individuals with diabetes and their loved ones, as it empowers them to take necessary steps in their daily lives to prevent and manage these conditions effectively. So, let’s delve into the world of diabetes-related health problems and discover the importance of proactive care.

Cardiovascular Problems
Heart disease
Diabetes is strongly associated with an increased risk of heart disease. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart, leading to various cardiovascular complications. These complications include coronary artery disease, heart attack, and heart failure. It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels to reduce the risk of developing heart disease.
Stroke
People with diabetes are also at a higher risk of experiencing a stroke. When blood sugar levels are consistently high, it can damage the blood vessels in the brain, increasing the likelihood of a clot formation or a vessel rupture. A stroke can lead to significant disabilities or even be life-threatening. It is important to control diabetes through proper management and lifestyle changes to minimize the risk of having a stroke.
High blood pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common complication associated with diabetes. The excess sugar in the bloodstream can damage blood vessels and make them less flexible, increasing blood pressure. Having both diabetes and high blood pressure can further escalate the risk of cardiovascular problems. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and medication, if necessary, can help manage both conditions effectively.
Kidney Complications
Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy refers to kidney damage that occurs as a result of diabetes. Elevated blood sugar levels can put excessive strain on the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste products from the blood. Over time, this can lead to kidney damage and eventual kidney failure. Early detection and management of diabetes can help reduce the risk of developing diabetic nephropathy. Regular check-ups, maintaining blood sugar levels within the target range, and managing blood pressure are crucial in preventing kidney-related complications.
Kidney failure
Kidney failure is a severe complication that can arise from diabetes. As the kidneys become more damaged due to diabetic nephropathy, they lose their function gradually. In advanced stages, individuals may require dialysis or a kidney transplant to maintain proper kidney function. Diabetes management, such as controlling blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol, is essential in preventing the progression of kidney damage and reducing the risk of kidney failure.
Eye Problems
Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a common eye complication of diabetes and a leading cause of blindness in adults. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, leading to vision problems and potential blindness. Regular eye exams, early detection, and proper management of diabetes are crucial in preventing or slowing down the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Cataracts
Cataracts, a clouding of the lens of the eye, are more common in individuals with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can cause changes to the lens, leading to the development of cataracts at an earlier age. While cataract surgery can effectively treat this condition, it is vital to manage diabetes to reduce the risk of cataract formation.
Glaucoma
People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing glaucoma, a condition that damages the optic nerve and can result in vision loss. The exact link between diabetes and glaucoma is still being studied, but it is believed that high blood sugar levels and changes in blood flow can contribute to increased eye pressure. Regular eye exams and proper management of diabetes are essential in detecting and treating glaucoma early to preserve vision.
Nerve Damage
Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage that commonly affects the feet and legs but can also involve other parts of the body. High blood sugar levels can injure the walls of the small blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the nerves, leading to nerve damage. Symptoms can range from tingling and numbness to severe pain and muscle weakness. Managing blood sugar levels effectively is crucial in preventing or slowing the progression of diabetic neuropathy.
Nerve pain
Nerve pain, also known as diabetic nerve pain or neuropathic pain, is a common symptom of diabetic neuropathy. The damaged nerves can send incorrect signals to the brain, causing pain and discomfort. This type of pain is often described as burning, tingling, or shooting. Medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes can help manage nerve pain and improve quality of life.
Digestive problems
Diabetes can also affect the nerves that control the digestive system, leading to digestive problems such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation. These issues can occur due to nerve damage or poor blood sugar control. Eating a healthy diet, managing blood sugar levels, and seeking medical advice can help alleviate digestive problems associated with diabetes.

Foot Complications
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, a type of diabetic neuropathy, affects the nerves in the extremities, primarily the feet. Nerve damage can result in the loss of sensation, making it difficult to detect injuries or wounds. Proper foot care, including regular inspection, wearing proper footwear, and maintaining good blood sugar control, is essential in preventing complications associated with peripheral neuropathy.
Foot ulcers
Foot ulcers are a common complication of diabetes, especially for individuals with peripheral neuropathy. When the skin on the feet becomes damaged or injured due to pressure or trauma, poor blood flow and reduced sensation can hinder the healing process, leading to the formation of ulcers. Prompt medical attention and proper wound care are crucial in preventing infections and complications associated with foot ulcers.
Infections
Diabetes can increase the risk of developing infections, particularly in the feet. Poor blood sugar control compromises the immune system’s ability to fight off infections, making individuals with diabetes more susceptible. Infections can occur through skin injuries or cracks, especially for individuals with peripheral neuropathy who may not feel the pain or notice the injury. Vigilant foot care, including regular cleaning, drying, and applying moisturizer, is essential in preventing infections and promoting overall foot health.
Skin Complications
Bacterial and fungal infections
Diabetes can make individuals more prone to bacterial and fungal infections on the skin. High blood sugar levels create an environment that promotes the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi. Common skin infections include bacterial infections such as staphylococcus and fungal infections like candidiasis. Maintaining good blood sugar control, practicing proper hygiene, and promptly treating any skin injuries or infections are essential in preventing skin complications associated with diabetes.
Itching
Persistent itching, also known as pruritus, can be a bothersome symptom for individuals with diabetes. Itching is often related to dry skin, poor blood flow, or nerve damage caused by diabetes. Managing blood sugar levels and using moisturizers can help relieve itching. It is important to avoid scratching, as it can lead to skin injuries and potential infections.
Dry skin
Dry skin is a common issue for individuals with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can lead to dehydration, which manifests as dry and cracked skin. Proper hydration, avoiding excessive bathing with hot water, moisturizing regularly, and managing blood sugar levels can help prevent and alleviate dry skin associated with diabetes.

Sexual and Reproductive Issues
Erectile dysfunction
Men with diabetes are more likely to experience erectile dysfunction (ED) than those without diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, impairing the blood flow to the genitals and affecting sexual function. Managing diabetes effectively, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking medical interventions, such as medication or counseling, can help address erectile dysfunction.
Low libido
Both men and women with diabetes may experience a decreased libido or sexual desire. Hormonal imbalances, nerve damage, and psychological factors can contribute to low libido in individuals with diabetes. Communicating openly with healthcare professionals and addressing underlying issues, such as managing blood sugar levels, hormone therapy, or counseling, can help improve libido and sexual well-being.
Fertility problems
Diabetes can contribute to fertility issues in both men and women. In men, diabetes can cause erectile dysfunction and reduce sperm quality and motility. In women, diabetes can affect hormonal balance and disrupt the menstrual cycle. Proper diabetes management, lifestyle changes, and seeking medical guidance are crucial in addressing fertility problems associated with diabetes.
Gum Diseases
Periodontitis
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing periodontitis, a severe gum infection that affects the tissues supporting the teeth. High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to fight off infections, leading to gum inflammation and tooth loss. Maintaining optimal blood sugar control, practicing good oral hygiene, and regular dental check-ups are important in preventing and managing periodontitis.
Tooth decay
Diabetes can increase the risk of tooth decay. High blood sugar levels create an environment that promotes the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth, which can lead to cavities. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, along with managing blood sugar levels, are essential in preventing tooth decay and maintaining oral health.
Mental Health Disorders
Depression
Depression is more prevalent in individuals with diabetes compared to the general population. Managing a chronic condition like diabetes can be emotionally challenging, leading to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or loss of interest. It is important to seek professional help, engage in self-care activities, and maintain a strong support system to address and manage depression effectively.
Anxiety
Anxiety disorders are also more common among individuals with diabetes. The constant worry about blood sugar control, potential complications, and the stress of managing the condition can contribute to anxiety. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises, regular exercise, and seeking therapy, can help alleviate anxiety symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Diabetes distress
Diabetes distress refers to the emotional and psychological burden associated with living with diabetes. The constant monitoring, medication, dietary restrictions, and potential complications can lead to frustration, overwhelm, or burnout. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, participating in diabetes support groups, and incorporating self-care activities can help manage diabetes distress and improve overall mental health.
Complications during Pregnancy
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It can increase the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby if not properly managed. Women with gestational diabetes may be more likely to develop high blood pressure, pre-eclampsia, and give birth to larger babies, which can lead to birth complications. Proper prenatal care, blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and potential medication are all important in managing gestational diabetes and minimizing associated risks.
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a condition characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs, commonly affecting pregnant women. Women with diabetes, particularly gestational diabetes, have a higher risk of developing preeclampsia. Regular prenatal check-ups, blood pressure monitoring, and close medical supervision are crucial in detecting and managing preeclampsia to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and the baby.
Preterm birth
Preterm birth refers to giving birth before the 37th week of pregnancy. Women with diabetes, especially those with poor blood sugar control, have an increased risk of preterm birth. Premature babies may face various health complications and require special medical care. Proper diabetes management and close monitoring during pregnancy are vital in reducing the risk of preterm birth and promoting a healthy pregnancy.